Recycling only works if waste is disposed of properly. In Germany, the different bins and containers can be quite confusing for many people. That’s why you can find everything you need to know about how to separate waste correctly in Germany here.
How to separate waste correctly in Germany?
With our overview, you can see at a glance how to dispose of your waste in the appropriate bin. In our article, we go into more detail about the individual bins, but also about the bottle bank and special waste.
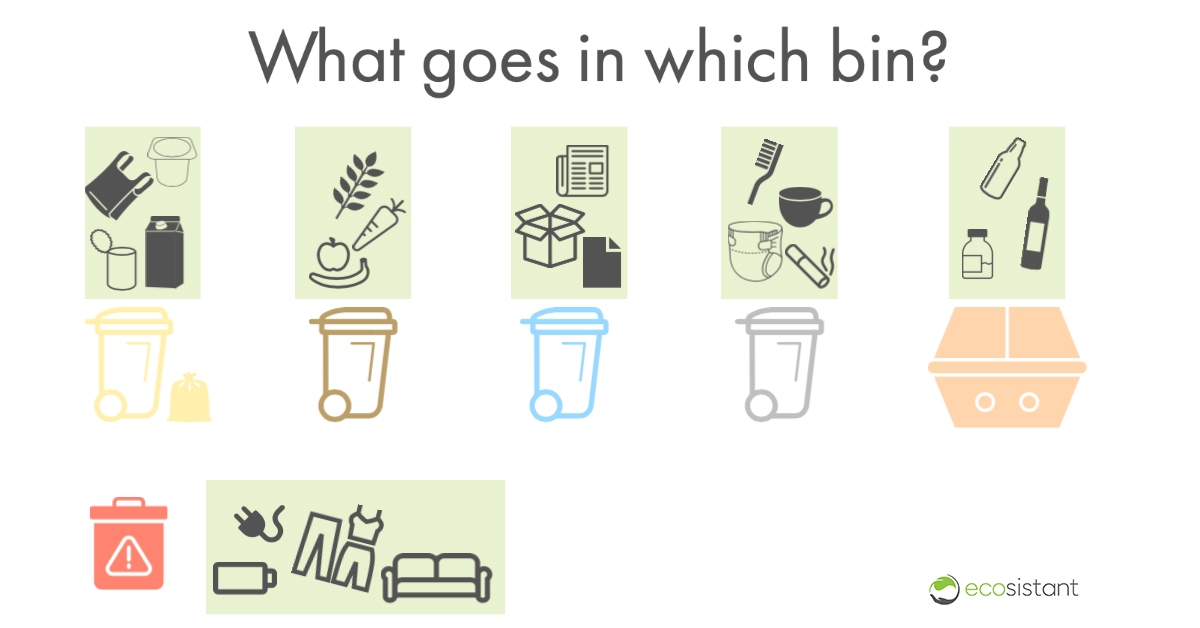
Yellow bin and yellow bag
Depending on the region, there is the yellow bin or the yellow bag. This is where packaging made of plastic, aluminium or tinplate belongs. In some communes there is a so-called “Wertstofftonne” (recycling bin). This is where plastic and metal that would not go into the yellow bin is also collected.
The basic rule is to dispose of waste loosely. In other words, remove the lid from the packaging and do not stack anything inside each other. This is the only way to recycle properly.
What belongs in the yellow bin?
- Beverage and milk cartons
- Foils
- Tins
- Plastic packaging
Brown bin
Organic waste belongs in the brown or green organic waste bin. This includes fruit and vegetable waste as well as other kitchen waste such as meat and bread scraps. Small amounts of garden waste such as grass clippings or cut flowers can also be disposed of in the organic waste.
Compostable plastic bags do not belong in the brown bin. They need two to three months to decompose. The rest of the organic waste only needs a few weeks to decompose.
Blue bin
Cardboard boxes, paper and newspapers go into the blue waste paper bin or the waste paper container. The same applies to blue sales slips, as they are not coated.
Greasy pizza boxes do not belong in the waste paper bin! They must be disposed of in the residual waste.

Black bin
Everything that can no longer be reused or recycled ends up in the residual waste. This waste is incinerated. This produces emissions, toxic slag and fine dust, and the waste is lost to further recycling.
Due to incorrect waste separation, only one third of the contents of the residual waste bin really consists of the waste that actually belongs in the black bin. This is not only bad for the climate and the environment, but also quite expensive to dispose of.
What goes into residual waste?
- Diapers
- Cigarettes and ashes
- Crockery
Bottle bank
Glass packaging for food, beverages, medicines and cosmetics is disposed of in the bottle bank. If a glass does not match the colour of one of the containers for white, brown or green glass, it is disposed of in the green glass container.
By the way: Always unscrew the caps from jars and dispose of them in the yellow bin. This saves energy later when recycling.
What does not belong in the waste glass?
- Window and mirror glass
- Drinking and wine glasses
- Light bulbs
- Ceramics
- Flower vases

Special waste
In addition to everyday household waste, special and hazardous waste also accumulates. These must be disposed of separately. Whether waste has to be disposed of at the bulky waste, recycling centre or special landfill depends on the respective product.
What must not be disposed of in household waste?
- Batteries
- Electrical appliances
- Clothing and other textiles
- Furniture
Electrical waste must be taken back by electrical shops and online shops. This puts the responsibility for disposal on the online retailers.
More sustainability through waste separation
Waste separation in Germany can seem overwhelming at first. But with a little knowledge, each individual can contribute to an effective recycling system.
You are an online retailer and wonder what responsibility you have through selling your products? With our compliance service, we can consult you about the recycling obligations in your target markets throughout Europe.
- Packaging licensing
- WEEE Directive
- Battery laws
