The German Packaging Act was amended again in July 2021. Part of the changes, however, will not get in force before next year. We have summarized in this article what changes producers, importers, and e-commerce sellers need to be aware of in Germany 2022 and beyond.
What is the Packaging Act?
The German Packaging Act (VerpackG) is the implementation of the European Packaging Directive 94/62/EC into national law. Through the Packaging Act, traders are made responsible to participate in the recycling of their product packaging.
The law on the marketing, return and high-quality recycling of packaging (VerpackG) has been in force since 2019. According to the Packaging Act, anyone who sells packaged products to private customers in Germany is obliged to participate in a dual system. These initial distributors must register with the packaging register LUCID and license their sales packaging there. Dual systems are nationwide take-back systems for this packaging.
To whom does the Packaging Act (VerpackG) apply?
Particularly affected by the law are:
- Commercially active producers, importers (to Germany), and (e-commerce) retailers,
- who put filled sales packaging into circulation,
- which accumulates at the end consumer (in Germany).
In short: traders and online traders who sell products that arrive at the end customer in sales packaging. Sales packaging is defined as product packaging, shipping packaging and service packaging.
What does this mean? Traders affected by the VerpackG have the responsibility to participate in the recycling of their packaging. Incidentally, the packaging licensing obligation does not apply to the B2B sector. In fact, the VerpackG mainly concerns the B2C business.
For all B2C online stores selling to Germany, our digital consulting service offers a simple step-by-step-guide free of charge.
We have already summarised more about the costs of packaging licences Germany in another blog post.
Which packaging must be licensed?
Regardless of their quantity, packaging must be licensed from the first circulation. This obligation therefore also applies to micro-enterprises. The Packaging Act states this obligation for packaging made of cardboard, plastic & Co. The resulting levies are used to finance the recycling systems. This means that a professional take-back and recycling of the packaging can be guaranteed.
What are the different types of packaging?
Transport packaging is packaging that is intended for the B2B sector, while packaging in the B2C sector is so-called sales packaging.
Product packaging protects the product directly from external influences
- Paper boxes
- Plastic packaging
Shipping packaging is used to protect the goods during transport
- Shipping cartons
- Cushioning material
- Filling material
Service packaging is used in catering and retail to hand over goods to the end customer
- Bread bags
- Pizza boxes
- Disposable tableware and to-go dishes
What happens if you are not registered in the packaging register?
Non-registration, non-licensing, or false quantity declarations are considered an administrative offence according to § 36 VerpackG. Depending on the violation, fines of up to 200,000 euros and a ban on distribution may be imposed.
In addition, the Central Packaging Register Office maintains a publicly accessible register in which all registered companies are listed. This transparency is intended to ensure fair competition. Incidentally, unregistered traders can be reported and then receive a warning.
Amendment to the Packaging Act: Changes for Fulfilment Service Providers
The amendment to the Packaging Act obliges fulfilment service providers such as Amazon to check their traders with regard to registration and licensing.
Note on the contents of the amendment:
The registration obligations for final distributors of service packaging and the extended registration obligation for obligated parties with information on all types of packaging they place on the market will only apply from July 2022.
On 3 July 2021, amendments to the register information and the possibility of authorisation for foreign companies without a branch in Germany have come into force. Details can be found here.
The VerpackG amendment will come into force in several stages
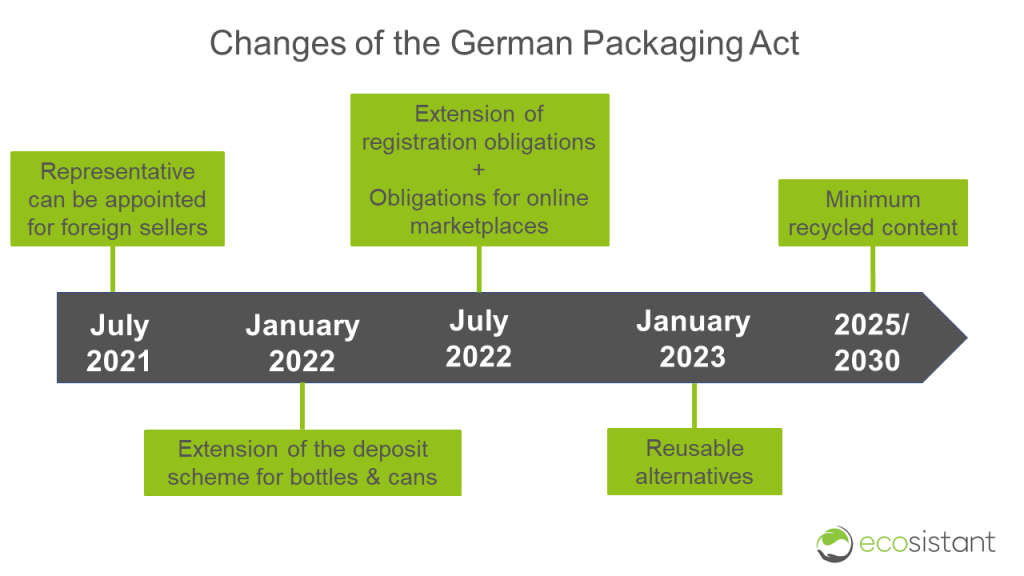
What will change in the Packaging Act from July 2021?
Since 3 July 2021, non-German companies that sell to end-consumers in Germany can assign an “authorized representative”. This representative needs to be a legal entity seated in Germany. It takes over all responsibilities in regards to the German Packaging Act on behalf of the foreign company. However, this is optional, and we recommend foreign businesses to fulfil their obligations by themselves without appointing a representative. We offer free step-by-step guides for all e-commerce businesses selling to Germany as part of our digital consulting service.
Furthermore, certain mandatory data when registering in the LUCID register has changed. For instance, it is now mandatory to provide a tax ID number in the register.
What will change in the Packaging Act from January 2022?
From 01.01.2022, the deposit obligation will be extended to previously exempt one-way plastic beverage bottles and beverage cans. An exception applies to products that entered circulation before 01 January 2022. These products may be sold to end consumers until 01 July 2022 without a deposit being charged.
What will change in the Packaging Act from July 2022?
From 01.07.2022, the extended registration obligation will apply for packaging that has previously been exempt. This affects (b2b) transport packaging, commercial packaging, returnable packaging, and packaging that contains dangerous substances or is an endangerment for the recycling process. If you place such packaging onto the German market, you are from July 2022 required to register in the LUCID-portal, although the packaging is still exempt from the “packaging license”.
B2B traders are required to take back empty packaging from their customers. They also need to inform their customers on the possibility to return packaging.
Another major change affects the operators and users of fulfilment service providers such as Amazon or Ebay. This is because online traders who use fulfilment service providers are now also obliged to register with the LUCID register and obtain the packaging license for shipping packaging. Electronic marketplace operators must check whether their traders are registered. Non-compliance will result in a ban on distribution.
What will change in the Packaging Act from January 2023?
From 01.01.2023, trade and gastronomy must offer reusable alternatives to disposable containers for to-go food and beverages. An exception applies, among others, to businesses with an area of less than 80 square meters.
What will change in the Packaging Act from 2025 and 2030?
From 2025, there will be a legally prescribed minimum recycled content for single-use plastic beverage bottles. From 2025, PET one-way beverage bottles must consist of at least 25% recycled plastic. From 2030, a recycled plastic content of at least 30% will apply to all single-use plastic beverage bottles.
Is recycling labelling mandatory on packaging in Germany?
Labelling for the identification of the packaging material is defined in VerpackG §6. The law proposes the use of the recycling code from the EU packaging waste directive. In a different way from the mandatory recycling labelling in Italy or in France, the marking is no obligation in Germany. It is only important that if packaging is marked with the material identifier, the correct code is to be used.
The responsibility of online retailers
The overarching goal of the German Packaging Act is to make manufacturers and retailers more accountable. Online retailers also bear responsibility for packaging and products they put into circulation. Therefore, it is important to report them properly. We are happy to advise you on your obligations as an online retailer. The advisory service for your recycling obligations in Germany is free of charge.
Photo by Karolina Grabowska from Pexels
Find information on packaging waste laws in other countries here:
Packaging law in France: a guide for e-commerce
Packaging law in Spain: Guidelines for e-commerce
Learn more about sustainable packaging in the following blog article:
Sustainable packaging for sustainable success
